hyperglycemia refractometer|diabetic eye refractive changes : import Hyperglycemia is the major cause of the transient refractive changes in diabetic patients. . (1) Read this entire manual before performing any services or repairs on this sterilizer. (2) Be sure you understand the instructions con-tained in this manual before attempting to service or .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Simply press the Start/Standby button and the Midmark M11 automatically fills with the correct amount of water. Select the cycle you want and the time is .
would it be proper to report that the pipette
refractive index for diabetic eyes
This study revealed that during treatment of hyperglycemia in diabetic patients, a transient hyperopic change of 0.5 diopter or more developed in all eyes. Hyperopic change gradually returned to the baseline value within four weeks in most patients.Hyperglycemia is the major cause of the transient refractive changes in diabetic patients. . This study revealed that during treatment of hyperglycemia in diabetic patients, a transient hyperopic change of 0.5 diopter or more developed in all eyes. Hyperopic change gradually returned to the baseline value within four weeks in most patients.
refractive index for diabetic
Hyperglycemia is the major cause of the transient refractive changes in diabetic patients. Following intensive medical treatment, a considerable number of patients tend to become more hyperopic compared with the hyperglycemic state.
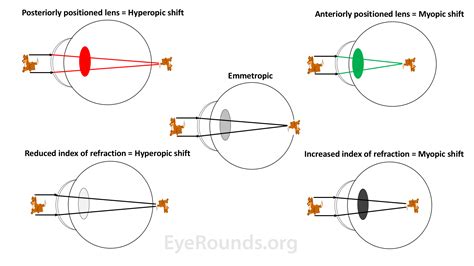
Treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus includes education, evaluation for micro- and macrovascular complications, attempts to achieve near normoglycemia, minimization of cardiovascular and other long-term risk factors, and avoidance of drugs that can exacerbate abnormalities of insulin or lipid metabolism. Hyperopic shifts (left side images) can occur if the lens is positioned too posteriorly or if there is a decrease in the refractive index of the lens. Myopic shifts (right side images) can occur if the lens is positioned too anteriorly or if there .
Acute hyperglycemia is associated with myopic refraction, but refraction becomes less myopic (or even hyperopic) with lowering of the levels of glycemia. 1-3 The distribution of refraction in a study of free-living persons with diabetes has not been well described. Some data are available from studies of eye diseases in general populations when .To quantify the retinal thickness and the refractive error of the healthy human eye during hyperglycemia by means of optical coherence tomography (OCT) and Hartmann–Shack aberrometry. Hyperglycemia was induced in five healthy subjects who were given .
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave owing to a change in its medium. The phenomenon of myopia during hyperglycaemia was first reported by Duke-Elder in 1925. 2 He suggested that the refractory changes were owing to osmotic pressure involving the lens. Results: Some studies have shown that increased blood sugar leads to a myopic shift whilst others demonstrated that this change is in a hyperopic direction. Changes in visual acuity in patients with diabetes could be an indicator of inadequate metabolic control or even the first sign of diabetes mellitus. This study shows that hyperglycemia generally does not cause changes in the refractive properties of the healthy eye. Nevertheless, in one subject a hyperopic shift accompanied by a change in shape and refractive index of the lens was measured.Hyperopic change developed a mean of 3.4 (SD 2.0) days after the onset of treatment, and reached a peak at 10.3 (6.1) days, where the maximum hyperopic change in an eye was 1.47 (0.87) D (range 0.50–3.75 D). Recovery of the previous refraction occurred between 14 and 84 days after the initial assessment.
This study revealed that during treatment of hyperglycemia in diabetic patients, a transient hyperopic change of 0.5 diopter or more developed in all eyes. Hyperopic change gradually returned to the baseline value within four weeks in most patients.Hyperglycemia is the major cause of the transient refractive changes in diabetic patients. Following intensive medical treatment, a considerable number of patients tend to become more hyperopic compared with the hyperglycemic state. Treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus includes education, evaluation for micro- and macrovascular complications, attempts to achieve near normoglycemia, minimization of cardiovascular and other long-term risk factors, and avoidance of drugs that can exacerbate abnormalities of insulin or lipid metabolism. Hyperopic shifts (left side images) can occur if the lens is positioned too posteriorly or if there is a decrease in the refractive index of the lens. Myopic shifts (right side images) can occur if the lens is positioned too anteriorly or if there .
Acute hyperglycemia is associated with myopic refraction, but refraction becomes less myopic (or even hyperopic) with lowering of the levels of glycemia. 1-3 The distribution of refraction in a study of free-living persons with diabetes has not been well described. Some data are available from studies of eye diseases in general populations when .To quantify the retinal thickness and the refractive error of the healthy human eye during hyperglycemia by means of optical coherence tomography (OCT) and Hartmann–Shack aberrometry. Hyperglycemia was induced in five healthy subjects who were given . Refraction is the change in direction of a wave owing to a change in its medium. The phenomenon of myopia during hyperglycaemia was first reported by Duke-Elder in 1925. 2 He suggested that the refractory changes were owing to osmotic pressure involving the lens. Results: Some studies have shown that increased blood sugar leads to a myopic shift whilst others demonstrated that this change is in a hyperopic direction. Changes in visual acuity in patients with diabetes could be an indicator of inadequate metabolic control or even the first sign of diabetes mellitus.
This study shows that hyperglycemia generally does not cause changes in the refractive properties of the healthy eye. Nevertheless, in one subject a hyperopic shift accompanied by a change in shape and refractive index of the lens was measured.
refractive changes in diabetics
refractive changes in diabetes lenses
would serological pipettes be equipment or materials
would you use density to calibrate a volumetric pipette
The speedy M7 autoclave is the perfect choice for anyone looking for an effective, manual .
hyperglycemia refractometer|diabetic eye refractive changes